1 B1 Thiamin in its functional form as TPP serves as a coenzyme in decarboxylation and transketolase reactions of carbohydrates. used in energy metabolism. It is involved in neurotransmission and nerve conduction.
Deficiency – Disease: Beriberi (wet with oedema; dry with muscle wasting), Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome in alcoholics can be deficient in thiamin. Syptoms: Enlarged heart, cardiac failure, muscular weakness, apathy, poor short-term memory, confusion, irritability, anorexia.
Pork, pork products, and enriched grains are reliable sources of thiamin.
2. B2 Riboflavin in functional form, FAD and FMN, used in energy metabolism, participates in a wide variety of oxidation-reduction reactions in numerous metabolic pathways that produce energy.
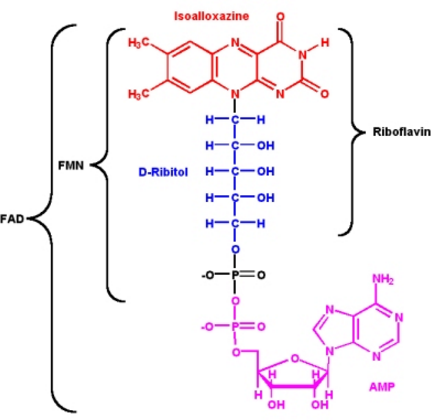
Deficiencies. Ariboflavinosis – symptoms sore throat, cracks and redness at corners of mouth, painful, smooth purplish red tongue (glossitis), inflammation characterised by skin lesions covered with greasy scales.
Dairy products and enriched grains are good dietary sources.
3. B3 Niacin as NAD and NADP are coenzymes. NAD is important in oxidation-reduction reactions that yield energy.
A deficiency of the vitamin produces the disease pellagra. Alcoholism can lead to a deficiency.
Food sources of niacin are enriched cereal grains and protein foods – Milk, eggs, meat, poultry, fish, wholegrain, fortified and enriched grains, nuts, The body is able to synthesize the vitamin from the amino acid tryptophan. Megadoses of niacin produce a variety of toxic symptoms.
4. Pantothenic acid in coenzyme form (CoA) shuttles two carbon fragments from the metabolism of glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, and alcohol into the citric acid cycle during energy metabolism.
Widespread in foods: chicken, beef, potatoes, oats, tomatoes, liver, egg yolk, broccoli, wholegrain.
If deficient: symptoms include: vomiting,, nausea, stomach crams, insomnia, fatigue, depression, irritability, reslessness, apathy, hypoglycaemia, increased sensitivity to insulin, numbness, muscle cramps and inability to walk.
5. B7 Biotin functions as a cofactor in four carboxylases, enzymes that add carbon dioxide to a substance. Used in energy metabolism, Amino acid metabolism and glycogen synthesis.
Biotin is widely distributed in foods; liver, egg yolks, soybeans, fish, wholegrains, and also produced by th GI bacteria
Deficiency: Depression, lethargy, hallucinations, numb or tingling sensation in the arms, and legs, red schaly rash around the eyes, nose and mouth, hair loss.
6. Vitamin B-6 Pyridoxine: in coenzyme form (PLP and PMP) participates in amino acid metabolism, especially the synthesis of nonessential amino acids.
Animal protein foods, vegetables, starchy vegetables, legumes, non citrus fruits, fortified cereals, liver and soy products are good sources of this vitamin.
- Deficiency: The four D’s are symptoms of Vit B6 deficiency: Scaly Dermatitis, microytic anaemia, Depression, Delirium -confusion and convulsions. and decreased immune response are symptoms of a deficiency. to the Extreme: Death.
- Toxic effects: depression, fatigue, irritability , headaches, nerve damagecausing numness and muscle weakness leading to an inability to wald and convulsions, skin legions.
7. Folate in one of its many coenzyme forms (tetrahydrofolic acid THF and DHF) accepts one-carbon groups from various donors and serves up one-carbon groups to a variety of metabolic pathways. The most notable job performed by folate is DNA synthesis, therefore very important in new cell formation.
A dietary lack of the folate produces megaloblastic anaemia, smooth red tongue (glossitis), mental confusion, weakness, fatigue, irritability, headache, shortness of breath, elevated homocysteine, and spina bifida and is one cause of heart disease (through the homocysteine link).
Deficiency is common among alcoholics and drug use.
Folate is found in green vegetables, legumes, liver, and fortified cereal grains. Folate is destroyed by high cooking temperatures.
8. Vitamin B-12 Cobalmin – Part of two coenzyme forms allows three-carbon fatty acids to be oxidized for energy and promotes normal red blood cell formation and helps maintain nerve cells. Because of its interaction with folate, a deficiency of vitamin B-12 results in the same type of megaloblastic anaemia, as well as excess homocysteine in the blood.
Vitamin B-12 occurs in animal foods but not in plant foods. Vegans need to look for foods fortified with the vitamin or take a supplement. Normally, the liver has a 5-year supply of vitamin B-12 in storage.
Defective absorption of vitamin B-12 is the cause of the deficiency disease pernicious anaemia, which frequently occurs in older adults. In such cases, megadose supplements or injection of the vitamin is necessary.
Deficiency disease: Pernicious anaemia ( caused by atrophic gastritis and lack of intrinsic factor not inadequate intake – deficiency can take 3-6 years to develop as the body stores reserves in the liver and muscles.
9. Vitamin C does not function as a coenzyme, like the B-vitamins. One of its many roles is in the synthesis of collagen, the protein used to form connective tissue. A deficiency of vitamin C causes the disease scurvy.
Fresh fruits and vegetable are reliable sources of this vitamin.
Like folate, vitamin C is destroyed by heat. Alcoholics and people who don’t eat fresh produce are most likely to develop a deficiency. Scurvy can develop. Megadoses of the vitamin causes gastrointestinal upsets but little else.
Precursors:
Choline is a dietary component that is available from a wide variety of foods and is synthesized in the body. No natural deficiency of choline has been reported. The amino acid methionine, vitamin B-6, vitamin B-12, and folate, along with choline, are intricately involved in the metabolism of the amino acid homocysteine. Elevated homocysteine in the blood is considered a risk factor for atherosclerosis.
Carnitine, inositol, taurine, and lipoic acid, while participating in many important biochemical reactions in the body, are not true vitamins because they can be synthesized in the body from readily available precursors, or obtained from the die